
ALL English verb tenses in 10 minutes!
Want to learn all the English verb tenses in less than 10 minutes? In this guide, we’ll cover the 12 essential verb tenses and their uses with examples. There’s a lot to unpack…
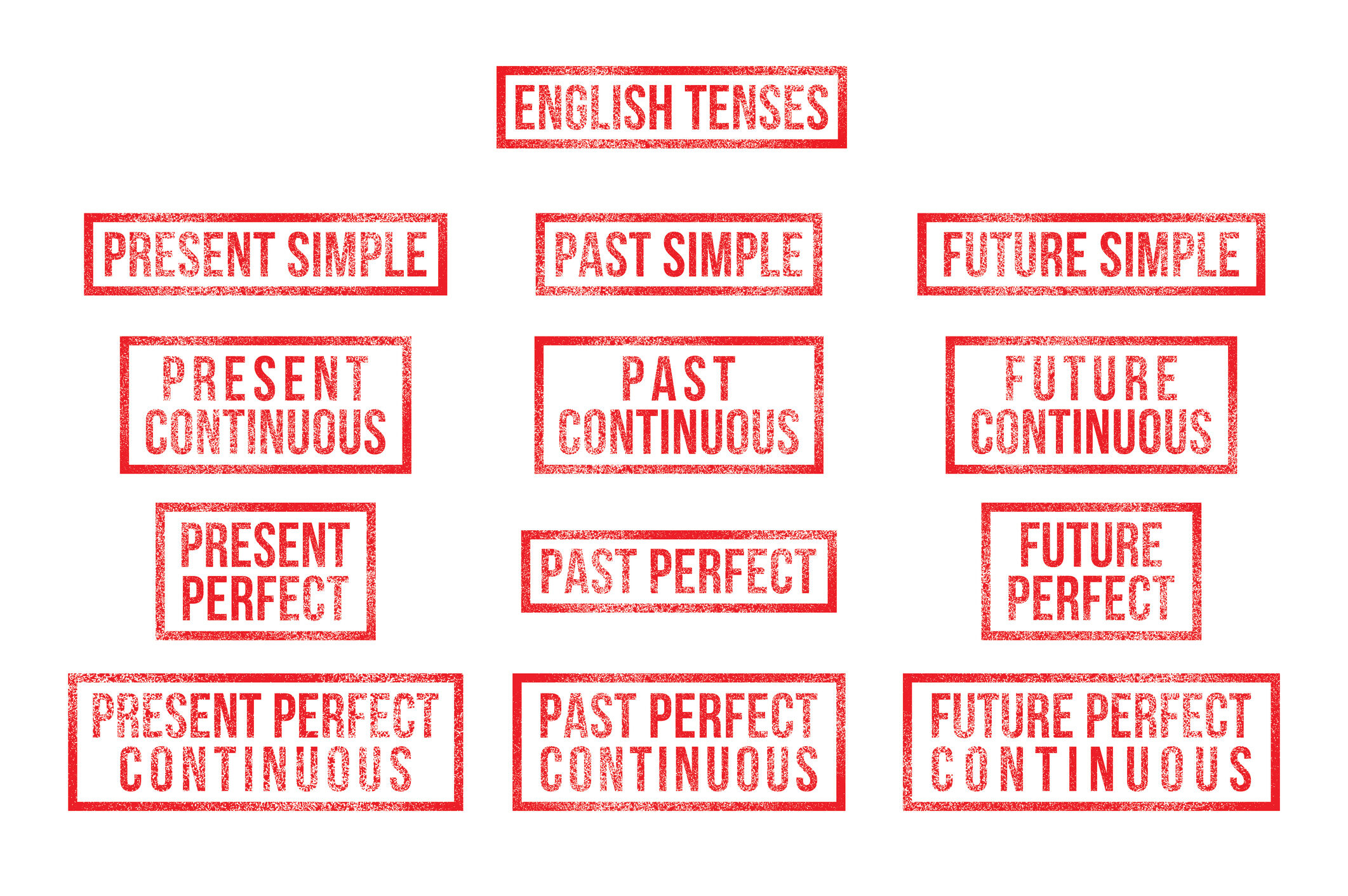
Overview of English Verb Tenses
To make it easy, let’s break down the verb tenses. We have past, present, and future, and each of these can be divided into simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms.
Present Tense
Present Simple: “I speak”
Present Continuous: “I am speaking”
Present Perfect: “I have spoken”
Present Perfect Continuous: “I have been speaking”
Past Tense
Past Simple: “I spoke”
Past Continuous: “I was speaking”
Past Perfect: “I had spoken”
Past Perfect Continuous: “I had been speaking”
Future Tense
Future Simple: “I will speak” or “I’m going to speak”
Future Continuous: “I will be speaking”
Future Perfect: “I will have spoken”
Future Perfect Continuous: “I will have been speaking”
This chart is available in the free PDF download. Now, let’s see some examples.
Present Tenses Explained
Present Simple
We use present simple for general facts and actions that happen regularly.
General Facts: “This shirt costs $10.”
Regular Actions: “I take guitar lessons on Wednesday nights.”
Your Turn: What is a general fact about yourself or your country? What is something you do regularly?
Present Continuous
Present continuous is used for actions happening right now or future plans.
Actions in Progress: “I’m studying biology at university.”
Future Plans: “I’m having lunch with Jack tomorrow.”
Your Turn: What’s something currently happening, and what’s something planned for the future?
Present Perfect
Present perfect connects past actions to the present.
Unspecified Time: “I’ve met several celebrities.”
Continuing Actions: “I’ve lived in this house for five years.”
Negative Experiences: “I’ve never broken a bone.”
Present Perfect Continuous
This tense is used for actions that started in the past and continue to the present.
“I’ve been thinking a lot about the situation recently.”
Past Tenses Explained
Past Simple
Simple past is for actions that happened and finished in the past.
“I worked as a research assistant from 2001 to 2003.”
Past Continuous
This tense is for actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past.
“I was taking a shower when you called.”
Past Perfect
Past perfect is for actions completed before another past event.
“By the time we arrived, the train had already left.”
Past Perfect Continuous
For actions that continued up to another past point.
“I had been working on some important projects before I lost my job.”
Future Tenses Explained
Future Simple
There are two ways to express future simple: using “going to” for plans and predictions, and “will” for promises and offers.
Plans: “I’m going to study for a master’s degree.”
Promises: “I’ll call you later.”
Future Continuous
This tense describes actions that will be in progress in the future.
“Don’t call me at 6:00 PM because I’ll be driving home from work.”
Future Perfect
For actions that will be completed before a future time.
“I will have written a book before I’m 40.”
Future Perfect Continuous
Used for actions continuing up to a future time.
“By the time she graduates, she will have been studying for seven years.”
Practice Makes Perfect
Many English learners find verb tenses confusing. But with practice, you can master them. The more you write, the easier it will be to remember the structures.
For more in-depth learning, including quizzes and feedback, check out my Advanced English Grammar Course available on my website Learn English at ease. Practice makes perfect!

Leave a Reply